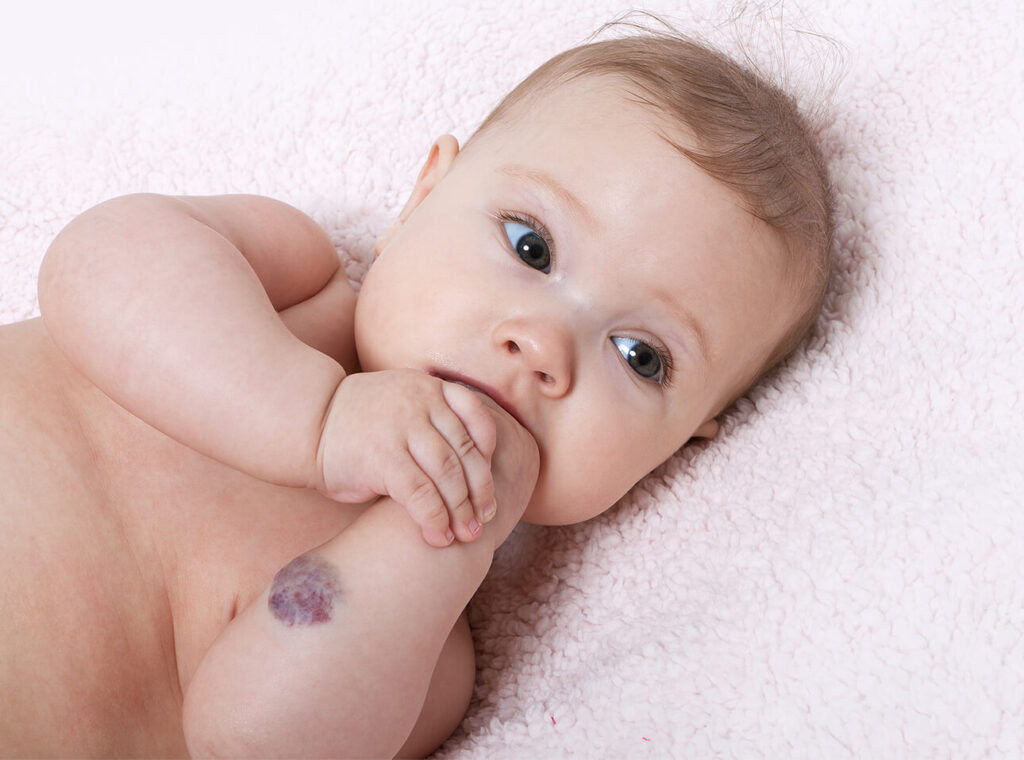
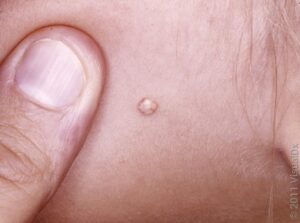
Hemangiomas and blood vessel tumors are the most common benign (noncancerous) tumors of childhood that most of the time resolve with no health sequela.
Hemangiomas are congenital meaning that the baby is born with them, or the lesion appears in the first few weeks of life. They grow for about a year and then start going away. A good rule of thumb used to be 10% per year so 50% are gone by 5 years and 90% by 9 years of age.
Since they involute (“resolve”), they are only harmful if in the process of growing they interfere with function of an organ. Examples are hemangiomas located on the eye that may interfere with vision development, on the nose or neck that may interfere with breathing, or in the mouth or genitalia.
Not every hemangioma needs treatment, but when they do, there are safe and effective medications to treat them. Most are a year-long course of topical or oral medications that are known as beta-blockers. Lasers are usually reserved for certain types of hemangiomas that break open and cause ulcers.
The caveat to the normal course of hemangiomas is that involution does not mean that every lesion disappears completely, and the skin goes back to normal. At times there is loose skin, a scar, or fatty tissue left in place of the involuting hemangioma.
This makes it very important to treat hemangiomas that can cause scarring or disfigurement and therefore lead to psychosocial issues in the child. Imagine if a large hemangioma is on the cheek of a child, it grows and then regresses but leaves behind a tuft of loose skin with fat and scar tissue- at that juncture the only option will be plastic surgery to remove the remnant tissue.
So, the simplified reassurance that usually parents hear “don’t worry about your baby’s hemangioma, it will go away with time” is not always valid. Rather, it is best to have a hemangioma evaluated by a pediatric dermatologist or dermatologist as soon as possible to determine the best course of action for each child.
Call Children’s Dermatology at (949) 679-1990 to schedule a consultation with Dr. Heidi Goodarzi. We will happily answer any questions and help determine an accurate diagnosis and the best treatment options for your family.